
 Many symbiotic and predatory relationships are relevant to the estuary biome. Here is an example of a common food chain in an estuary:
Many symbiotic and predatory relationships are relevant to the estuary biome. Here is an example of a common food chain in an estuary:Phytoplankton(producer)-Zooplankton(primary consumer)-Crab (Secondary consumer)-Fish(Tertiary consumer)-Human (Quaternary consumer). In the Chesapeake Bay estuary discussed before this chain is prevalent. On the left is a Chesapeake Bay food chain illustrating this. Above is a Chesapeake Bay food web.
These food webs and food chains illustrate common predator-prey relationships in estuaries. Several of these include:
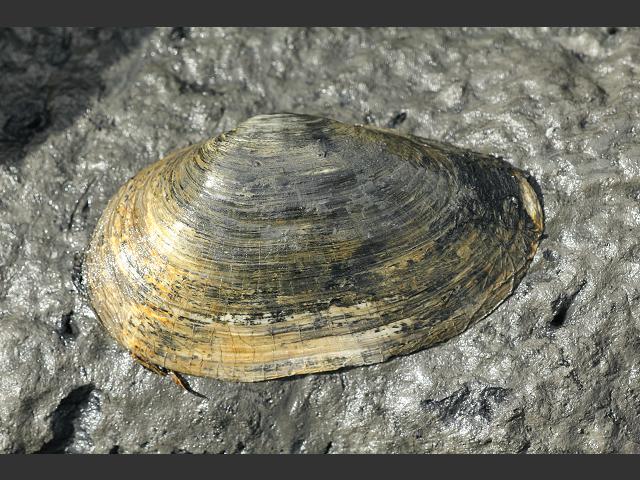
The Blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) and the infaunal clam prey (Mya arenaria).





Just FYI, your picture of a "rockfish" or Atlantic striped bass (Morone saxatilis) actually depicts a copper rockfish (Sebastes caurinus), which are found exclusively in the Pacific Ocean. There are a few species of Sebastes rockfishes in the Atlantic, but they are exclusively deepwater forms, and are bright red.
ReplyDelete-MLJ